Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the gums and the supporting tissues of the teeth. It is the leading cause of tooth loss among adults. Fortunately, effective treatments exist to slow its progression and protect your oral health. In this article, we explain what periodontitis is, the treatments adapted to its different stages, and the preventive habits that help avoid it.
What Is Periodontitis and How Does It Develop?
The Role of the Periodontium
The periodontium includes all the structures that support the teeth: the gums, the periodontal ligament, the alveolar bone, and the cementum that covers the roots of the teeth. These elements work together to keep the teeth firmly in place.
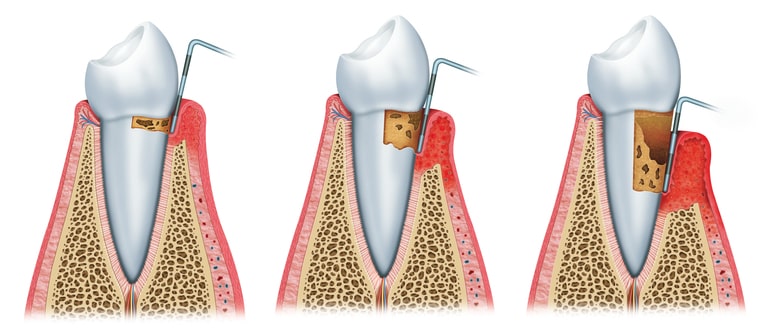
From Gingivitis to Periodontitis
When plaque and tartar accumulate and gingivitis is not treated, bacteria can slip under the gumline. This leads to periodontal pockets where bacteria continue to grow, gradually damaging the periodontium. Over time, this damage can result in tooth loss if not treated promptly.
Treatments Based on the Stage of the Disease
When periodontitis is diagnosed early, the main goal is to reduce pocket depth in order to eliminate bacteria and slow disease progression. This can be achieved with nonsurgical techniques such as scaling and root planing.
Root Planing
This treatment consists of deep cleaning the roots of the teeth to remove embedded tartar and bacteria. Local anesthesia is often used to ensure patient comfort. Smoothing the root surfaces helps prevent bacteria from accumulating again.
Open Curettage (Periodontal Surgery)
For more advanced cases, open curettage may be necessary. This surgical procedure involves lifting the gum to access deep pockets and remove tartar and bacteria. Once cleaned, the gum is repositioned to promote healing and reduce pocket depth.
Reconstructive Surgery
In severe cases where bone or tissues have been significantly damaged, reconstructive surgery may be considered. Various techniques can be used to restore tissues affected by periodontitis, including gum grafts and bone grafts. These grafts help improve the quality and stability of damaged tissues.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to help control bacterial growth in addition to mechanical or surgical treatments. Several approaches are typically combined to treat the infection while also addressing damage to periodontal tissues.
The Importance of Preventive Care to Avoid Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a serious disease, but it can be prevented with simple and consistent daily habits:
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and using dental floss
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and professional scaling
- Adopt a healthy diet and avoid tobacco, which worsens gum disease
By taking good care of your gums and your mouth, you can prevent gingivitis and stop it from progressing to severe periodontitis. If you have concerns about your oral health, schedule a consultation with our dentists in Montreal at the Centre Dentaire de Haute Technologie du Québec. We are here to answer your questions.