Periodontitis, an advanced stage of gum disease, is often underestimated until its effects become impossible to ignore. Yet this chronic infection can have devastating consequences—not only for your teeth and gums, but also for your overall health. Left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and is increasingly linked to serious systemic conditions.
In this article, we explain how periodontitis develops, the chain reaction it triggers in the mouth, and why early intervention is essential to protect both your oral and general health.
Periodontitis: Where Does It Come From?
Periodontitis develops from untreated gum disease, commonly known as gingivitis. Gingivitis is a mild inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of dental plaque—a sticky film rich in bacteria. At this early stage, the condition is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional care.
However, when plaque is not effectively removed, the bacteria multiply and the inflammation worsens. The infection then spreads deeper, attacking the periodontal tissues that support the teeth, including the gums, ligaments, and alveolar bone.
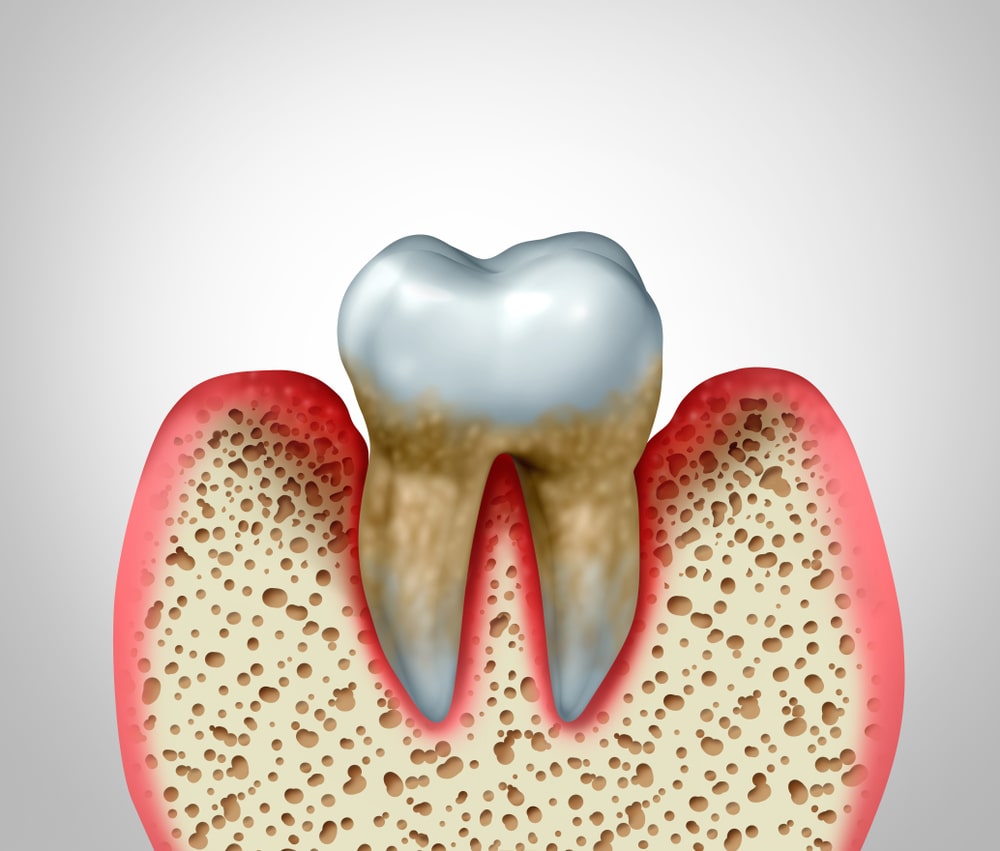
As the disease progresses, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, creating spaces known as periodontal pockets—an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive.
The Chain Reaction Triggered by Periodontitis
Formation of periodontal pockets
The detachment of the gums from the teeth creates periodontal pockets where plaque and bacteria accumulate. The deeper these pockets become, the harder they are to clean, allowing the infection to progress unchecked.
Irreversible destruction of periodontal tissues
Bacteria inside the pockets attack the periodontal ligaments and the alveolar bone. Bone loss at this stage is often irreversible, weakening the foundation that holds the teeth in place.
Tooth mobility
As bone and ligament support diminish, teeth may begin to feel loose or shift position. Patients often notice discomfort while chewing or changes in their bite alignment.
Tooth loss
Without treatment, ongoing bone loss eventually leads to tooth loss. At this stage, restoring oral function becomes more complex and may require advanced dental solutions.
Periodontitis and Its Impact on Overall Health
Periodontitis does not only affect the mouth. The chronic inflammation and bacteria associated with this disease can enter the bloodstream and may contribute to serious systemic conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Respiratory infections
- Complications related to diabetes
- Increased risk of cognitive decline, including dementia
Understanding Your Risk of Periodontitis
Not everyone has the same level of risk. Certain factors significantly increase the likelihood of developing periodontitis, such as:
- Smoking, which reduces the gums’ ability to heal
- A family history of gum disease
- Poor oral hygiene or irregular dental visits
- Chronic conditions such as diabetes that weaken the immune system
Identifying your personal risk factors is an important step in preventing periodontal disease.
Protecting Your Oral Health
The best way to prevent periodontitis is through early detection and regular dental care. Routine checkups allow your dentist to identify warning signs before irreversible damage occurs.
If you experience symptoms such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, gum recession, or tooth mobility, a consultation at the Centre Dentaire de Haute Technologie du Québec can help you protect your oral health—and your overall well-being.